When discussing healthcare standards, HIPAA often springs to mind first. However, the healthcare industry has a myriad of other standards designed to optimize communication and data exchange, improve care quality, and bolster patient safety. In today’s interview, we’ll delve into insights from Elinext experts regarding another pivotal standard in the healthcare industry — NCPDP.
What is NCPDP?
NCPDP (National Council for Prescription Drug Programs) is an organization that establishes data exchange standards for pharmaceutical drugs, supplies, and services within the US healthcare system. These standards help enhance safety, protect personal information, and improve the quality of medical care for patients and healthcare consumers while reducing system costs.
Quick facts about the organization:
- NCPDP is a non-profit standards development organization accredited by ANSI.
- Founded in 1977 in Scottsdale, Arizona.
- It has over 1,600 members representing most pharmacy sectors.
- NCPDP members develop solutions for the healthcare business through training and standards.
- NCPDP is also a forum for addressing healthcare issues, bringing together various stakeholders to enhance the exchange of medical information for patients and all those involved in providing medical care.
- NCPDP consults regulatory authorities, actively participates in the legislative process, introduces legislators to the NCPDP forum and its consensus-based solutions, and serves as a resource for directive bodies.
Who can become a member of NCPDP?
A member of NCPDP can become anyone interested in patient safety in relation to prescription drugs, anyone involved in the electronic exchange of information about medications, consumable materials, and pharmacy services, or anyone interested in integrating all areas of healthcare for the benefit of patients through information technology. The membership fee is $750 USD per person annually.
NCPDP membership allows its members to:
- Access standards as they are not freely available on the Internet.
- Participate in working groups and vote.
- Participate in educational programs, conferences, and webinars.
- Connect with colleagues, thought leaders, partners, and clients.
- Improve data quality in the organization using industry-developed products and services available only to member organizations.
What does the standard development process look like?
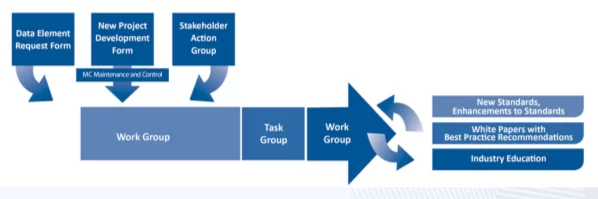
Generally, standards emerge from business needs and patient safety concerns raised by stakeholders at the NCPDP problem-solving forum. The forum can take the form of an initiative group of stakeholders, a working group, or an operational group. These groups can produce a variety of outcomes, from standards and reference materials to official documentation or best practice recommendations.
Once a standard is up for approval, bulletins are sent out to solicit public comments. Then the standards are approved by the Standardization Committee and the Board of Trustees. As needs are identified, standards are updated and refined or new ones are created.
Let’s talk more about working and operational groups since that’s where standards are created.
NCPDP comprises 10 active working groups that meet quarterly in different regions of the country. Quarterly working group meetings incorporate elements of training, committee interactions, activities of operational and target groups, networking events, leadership development, orientation of new members, and participation in exhibitions.
Currently, there are the following active working groups:
- Telecommunication
- Product identification
- Transaction standards between the manufacturer and the associated trading partner
- Government programs
- Professional pharmaceutical programs
- Electronic prescriptions and associated transactions
- Long-term and urgent care
- Specialty pharmacy
- Assessment of external standards and implementation guide
- Maintenance and management
Working groups often create operational groups. NCPDP has over 80 operational groups to execute specific projects and develop recommendations. Operational group leaders report on progress at the quarterly working group meetings. Both members of the organization and experts who are not members are invited to participate.
What is the target audience for NCPDP standards?
There are 3 groups of users:
Manufacturers/Providers – 28%
Pharmaceutical product manufacturers and long-term care service providers, all types of retail pharmacies (chains, independent institutions, online pharmacies).
Vendors/General Interest – 31%
Healthcare consultants, system providers, database management organizations, medical service organizations, professional/trade associations, wholesale drug distributors.
Payers – 41%
Pharmacy benefit management companies, medical insurance companies, state and federal agencies, as well as healthcare institutions.
NCPDP develops a vast number of standards and products. Here, we’ll focus on the main standards, and the two primary standards are the Telecommunication Standard and the SCRIPT Standard. With the adoption of those standards, the healthcare sector has seen annual savings around 30 billion US dollars. Studies have shown that electronic prescribing saves about 1 dollar in administrative costs and approximately 0.40 dollars on prescription refills.
Now, let’s take a quick look at the main NCPDP standards.
Billing Unit Standard (BUS)
This standard is designed for consistent and accurate billing of pharmaceutical products. BUS defines the standard measure for billing units of medications and provides recommendations for exceptional items. This is basically the billing language for pharmacy transactions. The core principle of BUS is that the quantity of each medication can be described as: “eaches”, “grams”, “or milliliters”.
Organizations involved in Digital Therapeutics should bring their product to the NCPDP billing department’s working group to verify the appropriate billing unit for their product based on its use. Manufacturers must complete a Quantity Unit Information Exchange (QUIC) form to help with the discussion and decision-making by the working group.
Product Identifiers Standard
The standard serves as a general guideline for consistent formatting and use of product identifiers within the NCPDP standards.
The following identifiers are adopted within the NCPDP standard:
- NDC (National Drug Code)
- NHRIC (National Health Related Item Code)
- HIBCC® (Health Industry Business Communications Council® Code)
- GTIN (Global Trade Identification Number)
- UPC (Universal Product Code)
- DI (Device Identifier)
- PIN (Product Identification Numbers)
Telecommunication Standard
A standard format for the electronic submission of drug claims from third parties and other transactions between pharmacy providers, insurance companies, third-party administrators, and other responsible entities.
The Telecommunication Standard encompasses such transactions as eligibility verification, pre-determination of benefits, claims billing, service billing, prior authorization inquiry, information reporting.
SCRIPT Standard
A standard for the electronic data transfer of prescriptions between pharmacies, doctors, intermediaries, institutions, and payers. The SCRIPT framework encompasses key business operations, such as the transfer of prescription information between a doctor and a pharmacy, as well as information about a patient’s medication history.
The standard supports data transfer for new prescriptions, prescription modifications, refill requests, prescription fill status notifications, prescription cancellations, and medication history. SCRIPT encompasses the following transactions:
- NewRx (New Prescription Transaction)
- RxRenewal Request/Response
- NewRX Request/Response Denied
- RXHistory Request/Response RxHistoryRequest
- RxFill Indicator Change
- The Prior Authorization (PA)
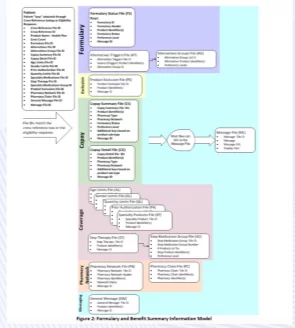
Formulary and Benefit Standard
The Formulary and Benefit Standard provides pharmacy benefit payers (including health insurance plans and pharmacy benefit managers) with the means to convey formulary and benefit information to prescribers through technology provider systems. It consists of a set of files with data about a patient’s prescription benefit plan.
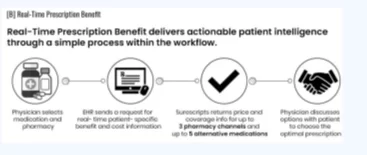
Real-Time Prescription Benefit (RTPB) Standard
The standard format for data exchange is designed to allow prescribers, pharmacies, and pharmacy claim processors to share information in real time regarding drug insurance coverage and the patient’s out-of-pocket expenses before prescription and medication dispensing. Thanks to the standardization of data elements and the data exchange process between the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) and intermediaries, there is significant potential for directly influencing price transparency and reducing out-of-pocket expenses for patients.
The standard enables the implementation of one or more real-time benefit tools that can be integrated with at least one electronic prescription system or Electronic Health Record (EHR) of a prescribing physician.
Benefit Integration Standard
The standard provides physicians at care delivery locations with information about patient benefits. It allows the transmission of accumulated data for various types of benefits across all medical service providers: pharmacies, primary medical institutions, dental and psychiatric clinics, and laboratories.
Are NCPDP standards mandatory?
Currently, NCPDP standards are advisory in nature. However, through recent legislative and regulatory actions, Congress and the federal government have recognized two NCPDP standards for use in the industry – a part of the SCRIPT standard regarding electronic prior authorization for specific drug coverage for a specific patient (ePA) and the Real-Time Prescription Benefit (RTPB) standard. Efforts are currently underway to establish these standards as mandatory at the federal level within the industry.
- The portion of the SCRIPT standard concerning electronic prior authorization (ePA) is cited in the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) regulation for use in Medicare Part D (Part D covers prescription drugs).
- The Real-Time Prescription Benefit (RTPB) standard is addressed in Section 119 of the Appropriations Act, directing the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to adopt the NCPDP RTPB standard as a tool for providing patients with real-time benefits.
As industry needs are identified, standards are updated to a new version or release. Standards Matrix provide an overview of the versions and releases of the most commonly used standards and implementation guides, as well as the NCPDP Data Dictionary and the List of External Codes.
Does NCPDP offer certification opportunities?
Currently, you can pursue the NSC-II certification from NCPDP. This is the V2017071 certification exam, based on the usage and practice of the new version of the SCRIPT standard. The exam is available online or during any of NCPDP’s quarterly working group sessions.
Certification is recognized as a professional credential for those who:
- develop and implement EHR systems;
- forecast risks and determine pharmacy policies;
- develop requirements and systems for pharmacies;
- determine product specifications;
- conduct training for project teams and end-users.
The exam helps implement the new version of SCRIPT, which was adopted on January 1, 2020.
Both members of the organization and non-members can take the certification exam and obtain the NCPDP certificate. Each certification exam consists of 119 questions and lasts 90 minutes. The cost is $325 for members of the organization and $575 for non-members. The certificate is only valid for a specific standard of a specific version; when a new version comes out, a new certificate needs to be obtained.
Does NCPDP work on anything else besides standards?
In addition to standards, NCPDP also develops and sells products and services. NCPDP’s informational products include:
- dataQ®: A reliable database with information on over 80,000 pharmacies.
- HCIdea®: A constantly updated database of more than 2.5 million prescribing physicians.
- resQTM: An industry resource for pharmacist qualification verification.
- RxReconn®: A legislative tracking product that allows real-time monitoring of legislative and regulatory activities related to pharmacy at both the state and national levels.
The bottom line
Just like other standards, NCPDP plays an important role in modern healthcare, streamlining data exchange and driving significant financial savings within the sector. At Elinext, our business analysts closely follow all applicable industry standards to help our clients navigate the intricate landscape of healthcare and pave the way for safe and more patient-centric care delivery.