We continue exploring 5G technology usage in healthcare. After covering the most obvious use cases we are down to explore the more complex ones. Get ready to dive into the world of remote procedures, robots, and big data.
Ericsson Research on 5G in Healthcare
One of the leading telecom companies of the world has conducted research concerning the use of technology.
75.7 billion US dollars will be involved in healthcare digitization with the help of 5G technology by 2026.
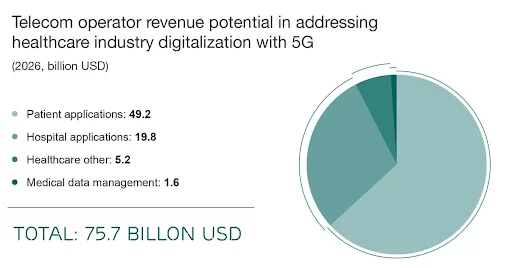
Source: ericsson.com
Let’s dive into use cases of 5G in modern-day healthcare and not-so-far future.
Hospitals Turn into Data Denters
In order for the transformation of patient applications to happen, patient data will need to be stored centrally, effectively turning hospitals into data centers and doctors into data scientists. Patients will get online access to a central repository of medical records to help them easily manage the quality and efficiency of their care.
45 percent of the cross-industry experts consider this a breakthrough in healthcare provisioning, while 47 percent of telecom decision-makers say that secure access is a key challenge.
Performing Remote Procedures
Robotic surgery is already happening today in operating theatres, but with the surgeon standing next to the robot rather than remotely. Nearly half (48 percent) of consumers feel that remote robotic surgery would be acceptable yet sixty-one percent believe such procedures are risky as they rely on the internet.
Such procedures are conducted using haptic feedback and high definition image streaming demanding low-latency and high throughput communication.
5G networks are essential to the provision of remote services yet the demands from the evolving healthcare sector on technology are high.
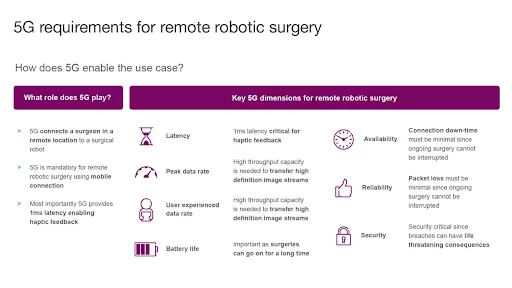
Source: ericsson.com
The robotic surgery market is currently valued at more than $3 billion and is expected to surpass $7 billion by 2025, according to data from iData Research.
The potential for this market is driving medical device manufacturers to invest heavily in medical robotic systems. Medtronic acquired Mazor Robotics, a developer of spine surgery guidance systems, for about $1.64 billion in September.
Johnson & Johnson dove deeper into robotic surgery with a $3.4 billion deal to acquire Auris Health, the Silicon Valley designer of endoscopic hardware aimed at lung cancer.
Intuitive Surgical currently dominates the surgical robotics market and claims every 36 seconds its da Vinci robotic system helps a surgeon perform better. The company’s robots have been used in 5 million minimally invasive surgeries as of the end of 2017, with 43,000 trained surgeons and 4,400 systems installed including in 100% of the top hospitals for cancer, gynecology, gastroenterology, and urology, according to the company.
Most robotic platforms are intended to streamline the surgical process, increase safety, and reduce complications, often through a minimally invasive approach, according to the Fitch Solutions report.
“Currently, robotic surgery is utilized in few countries and in advanced medical facilities; however, surgical robotics are evolving so that they are more widely accessible,” the report says.
Current robotic surgeries also require the surgeon to be located in the immediate vicinity of the patient where they can control the robot via a monitor. Surgical robotics manufacturers are increasingly incorporating 5G capabilities into these devices, which could vastly expand how these systems are used.
“With the adoption of 5G networks, which allow near-instantaneous communication due to low latency, surgeons will be able to perform remote procedures that are impossible today due to geographic limitations or critical timing requirements such as blunt trauma/accident injuries requiring operative procedures in ambulances and in war zones,” the authors of the report said.
The use of robotic-assisted surgery also could help patients in remote locations without surgical specialists or in developing countries where per capita specialists are limited, the report said.
A surgeon in China has already performed the world’s first remote operation using 5G technology, according to PCMag, citing local reports from China. The doctor in the southeastern province of Fujian used the next-generation network to control robotic arms in a remote location 30 miles away. The surgery was made possible by the extremely low latency of 5G.
A current drawback for the mass rollout of this technology and a guarantee in a wider service usage is the requirement of haptic feedback.
“In the past surgical robots have not had haptic feedback but that is changing as manufacturers understand the importance and incorporate it into their devices,” the authors of the report said.
Engineers and surgeons at the University of Naples Federico II in Italy, using Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci Research Kit, have now developed a force sensor for the da Vinci trocars that provides real-time haptic feedback to the user, according to the report.
Source: floridatoday.com
“The surgical instruments stay as they are and don’t have to be modified in any way, making it easy to introduce the technology into future surgical robots,” Fitch Solutions said.
The report forecasts that multimodal sensorial inputs especially along with haptic feedback enabled by 5G and other innovations will lead to wider usage and revolutionize the quality, cost, and availability of healthcare.
The first large surgical robotics company to incorporate haptic feedback will capture a large market share which will likely result in greater competition in the surgical robotics industry as well.
5G infrastructure is still in its infancy around the globe, and that currently limits the availability of the technology. In the U.S., AT&T, Verizon, and other carriers are starting to launch 5G networks this year, with 5G services for business already rolling out in some markets.
Rush University Medical Center and AT&T announced in January that Rush would be the first hospital in the nation to move to 5G.
As the technology improves, so will the scope for these surgical robots, Fitch Solutions said.
Moving forward, surgical robotic manufacturers will have to work alongside telecommunications providers to ensure new systems are designed to be able to keep up with the technological innovations that are taking place, the authors of the report said.
Remote Monitoring
When it comes to battery life, 42 percent of cross-industry decision-makers expect 5G to enable devices to consume less power which is key in remote monitoring situations.
Current consumer-grade wearables are widely used for preventative measures but are not considered sufficiently accurate or reliable for diagnosis. In addition, for liability reasons, patients’ smartphones cannot be relied upon for connectivity. For their part, wearables require high-frequency updates from a central repository but at low-data rates.
5G connectivity is not limited to wearables; it also enables patients to carry a medical-grade 5G router that then connects to various wearables using Bluetooth.
Emerging Technologies are Vital to Healthcare Transformation
5G will enhance many existing use cases while creating new ones unfulfilled by current technologies, such as remotely performed patient examinations and even operations. What’s also certain is that critical healthcare services require reliable connections. Very low end-to-end latency and ultra-reliable communications will prove essential to the provision of instant communication regarding patients’ conditions – through HD images and access to medical records – and provide accurate feeling and tactile interaction in the case of remote surgical procedures.
The following emerging technologies could be called vital to healthcare transformation:
- 5G New Radio interface and access must extend beyond those of previous generations of mobile communication, with massive system capacity, extremely low latency, ultra-high reliability and availability, and very low device energy consumption.
- Federated Network Slicing enables the roaming of network slices in other networks to provide global reach for services.
- RAN virtualization and Distributed Cloud ensure very low end-to-end latency. Artificial intelligence and real-time machine learning analytics will become important elements of making the networks self-optimizing to secure the fulfillment of service-level
Conclusion
As one could imagine, 5G adds speed up. This additional speed will enhance many existing use cases. It would also create new ones that can’t’ exist under the current technology stack.