The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has had a profound impact on the development and implementation of AI systems. The impact of GDPR on AI compliance: by 2025, 70% of AI projects will integrate privacy principles embedded in the design to comply with GDPR requirements, and fines for non-compliance can reach €20 million, or 4% of global turnover. AI Software Development Services are now prioritizing explainable AI (XAI), data minimization, and robust consent mechanisms. An AI-powered recruitment tool must not only avoid discriminatory results but also provide candidates with the right to explain, ensuring compliance with both ethical and legal standards.
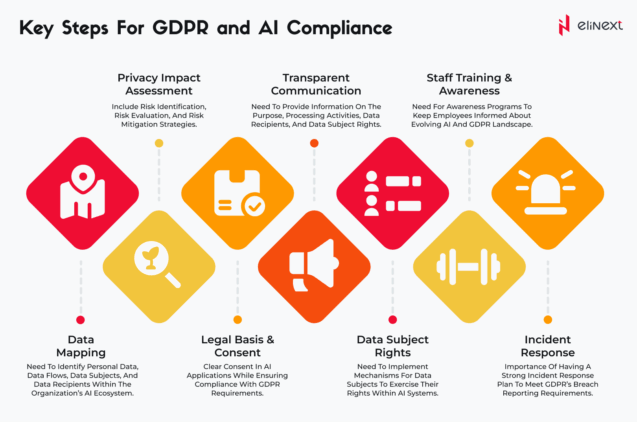
GDPR impact on AI. What is the GDPR?
What’s the GDPR, anyway? The General Data Protection Regulation is an EU-wide data protection law that changes various national privacy laws. The EU enacted the law two years ago, but it came into effect on May 25, 2018. Let’s outline its significant points:
- Companies collecting personal data must explain what it will be used for. Therefore, they don’t have a right to use it for anything else;
- They should minimize the amount of data they collect and keep. There’s a time limit for keeping as well;
- Users have a right to request the information on how precisely their personal data is used;
- Companies must notify its customers of data breaches in 72 hours;
- Customers can also demand a complete removal of their data upon request;
- If personal data is used to make automated decisions, companies must be able to explain the logic behind the decision-making process;
- Companies dealing with particular categories of sensitive data such as medical records or children’s data should be especially careful.
“Big data challenges purpose limitation, data minimization and data retention – most people never get rid of it with big data,” continues Edwards. “It challenges transparency and the notion of consent since you can’t consent lawfully without knowing to what purposes you’re consenting… Algorithmic transparency means you can see how the decision is reached, but you can’t with machine-learning systems because it’s not rule-based software.”
Address the GDPR impact on AI proactively!
Focus on developing AI solutions that ensure privacy, transparency, and accountability to ensure compliance and build user trust.
Now let’s observe some possible effects of the GDPR impact on AI businesses:
– GDPR impact on AI: the overall cost of AI will go up.
In accordance with Article 22 of the law, companies are obliged to assign humans to review certain algorithmic decisions. This restriction is regarded as the most painful, as it will lead to the significant raise of labor costs. Secondly, it works in the exact opposite direction from the initial idea. After all, the main reason for developing AI and ML software development solutions is to automate functions that would otherwise be much slower and costlier.
– GDPR and artificial intelligence: Damaged AI Systems.
As a rule, AI systems, which “learn” from the data they process must “remember” all the data they used to train themselves in order to sustain rules derived from that particular data. However, the Article 17 provides the right to erase it. This way, it will affect AI system’s behavior, and, consequently, make it less accurate or, in the worst-case scenario, fully damaged.
– GDPR impact on AI: Increased regulatory risks
Again, there’s a strong suspicion that small and medium-sized businesses won’t understand the regulation in full measure. The fines are pretty draconian, to say the least: up to 4% of a company’s global turnover, or €20 million (depending on which number is greater). Naturally, such a fine is more costly for small businesses, thus the chance of adopting AI software development solutions for them is becoming even lower.
So the question is: “What can they do to survive in those circumstances?” First of all, a company should become aware of what data it controls and where it is stored. This job will require collective efforts of a whole organization: top management, IT department, and human resources team among them.
Tim Estes, founder and president of Digital Reasoning, said that “The GDPR is a big deal for AI because it necessitates that we think differently about how we collect and use data. For too long, tech companies have insisted that in order to receive value from their products and services, you had to give up your data.”
Secondly, the GDPR will strengthen the versatility of AI in regard to fraud prevention and breach detection. The detection of cyber threats by AI will protect the rights of customers and serve legitimate interests as stated in Article 47 of the GDPR. Consequently, it will stimulate higher investments in AI cybersecurity.
In third place, the adoption of the GDPR might reconcile the providers of AI-powered service and its users as providers will become more responsible for how and where they use data resources.
“At the end of the day, AI providers should only need to own the algorithms — not the data — to innovate their capabilities and solutions.” summarizes Estes.
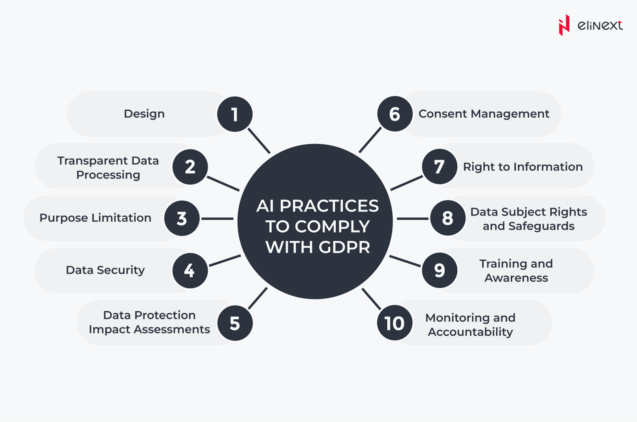
The GDPR impact on AI is a game-changer. AI integration services must prioritize privacy, explainability, and effective data governance. Organizations need to implement GDPR requirements from the outset, ensuring ethical AI development and avoiding harsh fines. This is about building trust and responsible innovation.
Quote from an Elinext expert
Conclusion
GDPR compliance is not just a legal checkbox but a driver of responsible innovation. Chatbots Development Services and other AI solutions routinely embed privacy-by-design, explainability, and robust data governance. Adherence to GDPR principles like data minimization and purpose limitation is now standard, ensuring AI systems respect individual rights, build trust, and avoid significant legal penalties. This fosters a culture of ethical, transparent, and user-centric AI development.
As artificial intelligence becomes more deeply ingrained in our lives, the impact of GDPR on AI compliance will only increase. Companies that utilize Generative AI Development Services to create ethically sound and legally compliant systems will not only avoid penalties but also earn customer trust, creating a sustainable competitive advantage in the AI-powered economy of the future.
FAQ
What is the GDPR?
The GDPR is an EU law governing personal data protection. The GDPR impact on AI: it mandates consent for data processing, directly impacting how Generative AI Development Services handle user data for model training and deployment.
Why is the GDPR relevant to Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI systems process vast amounts of personal data. The impact of GDPR on AI compliance: GDPR requires transparency, accountability, and data protection, making ethical and legal AI development essential—especially for automated decision-making.
What are the main GDPR principles that apply to AI systems?
Key GDPR Principles for AI Lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability. AI must only collect and process necessary data, and do so transparently.
What is “automated decision-making” under the GDPR?
When AI makes decisions without human intervention that significantly affect individuals (e.g., an AI loan system denying credit), GDPR grants individuals rights to explanation and human review.
How does the GDPR regulate profiling in AI?
The GDPR impact on AI: profiling by AI that leads to significant effects must be fair, transparent, and allow individuals to object or request human intervention (e.g., AI profiling job applicants).
What rights do individuals have under the GDPR regarding AI systems?
GDPR grants rights to access, rectification, erasure, restriction, portability, and objection—especially for AI-driven decisions. GDPR and artificial intelligence: users can request explanations for AI decisions affecting them.
How can AI developers ensure GDPR compliance?
AI developers must implement privacy-by-design, conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), minimize data, build explainable AI, and establish robust consent mechanisms. Anonymizing data before model training.
How do ethics relate to GDPR compliance in AI?
GDPR enforces ethical AI by requiring fairness, transparency, and accountability. An ethical AI system naturally aligns with GDPR’s non-discrimination and data protection mandates.