In March 2022, hackers stole data of 2 million patients from 60 healthcare institutions in order to sell it on the black market for $10-60 per piece of information. By comparison, credit card information costs about $1 for a piece. Hunting for medical information is explained by the fact that it contains personal details, date of birth, address, diagnoses, social security numbers, and much more. Then it can be used to get fraudulent prescriptions or cheat an insurance company. By the way, US consumers lose $80 billion every year due to insurance fraud.
To gain access to the network of healthcare institutions, cyber criminals use various methods, such as phishing or ransomware. For example, a healthcare organization employee receives a letter asking to follow a link and enter particular data that goes into the hands of attackers. By clicking on the link, users install malware into the system, which can change electronic documents or block medical devices. Then hackers squeeze money for decrypting data or unlocking equipment. In 2018, Hancock Regional Hospital paid intruders $47 thousand to unlock its network.
IBM revealed that data breaches cost healthcare institutions $6.45 million in 2019. It’s no wonder that medical organizations are looking for ways to protect their databases. Zero Trust is one of the methods that can provide security to their systems and resources. The approach was developed by former Forrester analyst John Kinderwag in 2010. Let’s take a look at this model and find out why health app developers should take it into account.
What Is Zero Trust and How Does It Work?
Zero Trust is a model that is based on the principle of “trust no one, always verify.” It is assumed that all users or devices that access healthcare providers’ resources are considered insecure by default and must be verified every time. All their actions should be monitored and supervised constantly. This applies to both internal and external users and devices. This approach allows you to minimize the risk of security incidents.
What Does Zero Trust Protect?
Data
The Zero Trust model primarily protects data that is the main target of most hackers. Therefore, healthcare organizations must be able to classify, analyze, track, and protect their confidential information. To do this, they should use various measures, such as multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and access control. In addition to these measures, specialized solutions can be used. Many different tools that are aimed at protecting confidential information are available in the market today. For example, there is DLP (Data Loss Prevention) software that is used to prevent accidental and intentional data leakage. Statista shows that the DLP market is growing and is expected to reach $3.5 billion by the end of 2025.
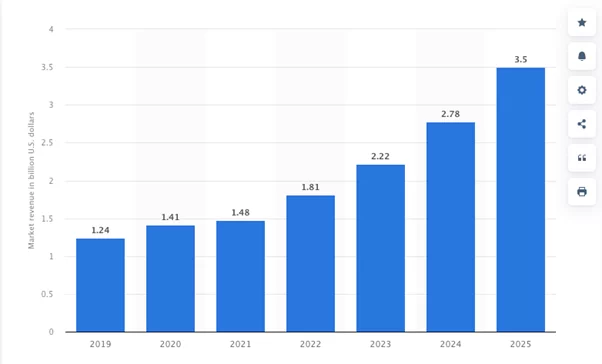
Source: Statista
Corporate Networks
Organizations usually transfer their data across corporate networks. Hence, in order to steal confidential information, cybercriminals should infiltrate a corporate network, find the data, and take it outside the perimeter. According to the 2021 Healthcare Cybersecurity Survey, 70% of respondents told that their medical corporate networks have experienced major security breaches in the past 12 months.
In order to prevent attackers from floating the corporate networks, one should segment and isolate them using special equipment, such as firewalls, managed switches, vulnerability scanners, SIEM (security information and event management), and others. Segmentation involves creating different virtual groups for various elements.
For example, access systems and CCTV cameras can be included in one group, IoT medical devices in another, financial departments in the third one, and so on. Then certain employees get access rights to these groups. This measure ensures better data protection because the number of persons working with private information will be limited.
Users
Users are the most vulnerable cyber security element. They constantly exchange data with each other, including various analyzes, images, drug orders, and much more. That’s why it’s important to define the rights and privileges for each user group. It will be useful to apply a VPN connection and CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) to ensure secure access to the resources. Moreover, there are various tools to manage user rights, such as PAM (Privilege Access Management) and others. ResearchAndMarkets found that the global VPN market is expected to reach $46 billion in 2022.
Workloads
The workload includes backend software and all medical applications that are used by patients. Apps must be constantly updated and tested for faults. Otherwise, hackers will be able to easily break into them and steal confidential information. Thus, healthcare providers should choose proven developers who use Zero Trust and other measures to build secure solutions. To ensure app security and monitor and identify vulnerabilities in workloads, patch management software, applications management software, and other tools can be used as well.
Devices
The IT infrastructure of any modern healthcare institution includes a great number of devices, such as printers, scanners, portable medical devices, IoT devices, and so on. Moreover, the healthcare organization’s networks include new types of devices, such as wearables, health apps, patient monitoring systems, smart wheelchairs, and others. They also should be protected from hacker attacks. Therefore, medical institutions should use secure solutions and apply various tools (e.g., mobile device management software, device control management software) to monitor and segment all devices connected to their networks.
How to Implement Zero Trust in Healthcare?
According to Okta, 54% of healthcare institutions plan to implement the Zero Trust model within the next 12 to 18 months. How to make it effective? To do this, they should define a protection surface, which includes the most important data, applications, services, and so on. The smaller the attack surface, the more difficult it’s for hackers to gain access to the assets. Then they should carefully examine how users use their systems and update permissions as required.
The next step is to create a clear policy that describes who can access each group of your IT systems and how. With this policy, healthcare institutions will be able to control access, as well as manage and prevent security incidents. When the zero perimeter network is established, they should constantly monitor and update it to keep their resources secure.
The third option is to choose Zero Trust-based healthcare solutions. The Zero Trust security software market size reached $18.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow to $64.4 billion in 2027, according to ResearchAndMarkets. Seeing that the interest of healthcare institutions in Zero Trust is growing, healthtech software developers should take this model into account when developing their products, such as EMR/EHR systems, telehealth solutions, mHealth apps, and so on. HIPAA requires all medical products to be safe and secure. With Zero Trust, healthcare software development companies will be able to provide a higher level of protection for their products.
How to Implement Zero Trust into the Software Development Process?
Zero Trust is not a technology or a solution; it’s a set of ideas and requirements for protecting corporate networks and data. They include multi-factor authentication, data encryption, segmentation, risk assessment, application classification and grouping, user behavior analysis, device, and system status analysis, system status monitoring, process automation, continuous protection of devices and resources from threats, and so on. Accordingly, all these measures can be implemented by the developers of medical products.
Applying the Zero Trust approach will allow development companies to improve the security of applications and make them less vulnerable to cyber attacks. To do this, developers should:
- Identify their users (employees, customers, testers, etc.) and give them certain access rights;
- Identify all devices connected to the networks (PCs, laptops, printers, CCTV, employees’ devices, etc.) and segment them; and
- Carefully assess the risks (e.g., using clouds, working with freelancers, etc.).
- Create more secure apps. For example, use proven libraries and tools and special instruments in order to analyze them.
Bottom Line
2021 Zero Trust Adoption Report from Microsoft showed that Zero Trust is gaining popularity. 90% of respondents are familiar with this approach, and 76% are implementing it right now. The key principle of Zero Trust is that any information can be compromised. This means that you need to carefully check the security of accounts, endpoints, networks, and other resources based on all available signals and data. It’s especially important to apply Zero Trust in healthcare since medical institutions process a huge amount of confidential information today.
Forrester Consulting revealed that only 22% of developers clearly understand how to appropriately comply with the security policies. If you or your company needs help with cyber security issues, the Elinext professional team is ready to answer all your questions.