For years, cyber attacks against healthcare institutions have been growing more sophisticated, complex, and frequent. In 2021, cybersecurity breaches hit an all-time high, exposing personal health information (PHI) of over 45 millions people.
Industry experts believe that 2022 can be even worse as cybercriminals recognize that healthcare entities are a lucrative target. We are only halfway through the year, and there are already high-profile cases that underscore the gravity of the situation.
- On January 2, Florida-based Broward Health reported that it had suffered a breach affecting more than 1.3 million people;
- Shields Health Care Group said that an unknown party gained access to personal data of 2 million patients;
- South Denver Cardiology Associates announced that in January it fell victim to a cyberattack that affected over 280,000 patients;
- In March, Norwood Clinic started sending letters to 228,103 current and former patients, notifying them of a hacking incident;
- Logan Health Medical Center also started notifying certain patients about a data breach, and a respective report suggests that the PHI of up to 213,543 individuals was compromised;
- Tenet Healthcare, one of the largest health systems in the US with 60 hospitals and 550 care centers, announced that in April a cybersecurity incident disrupted some of its acute care operations.
In addition to the bad reputation that imminently follows, healthcare data breaches are the costliest. According to IBM, an average data breach cost has increased by $2 million and has reached $9.42 million per incident.

Source: Compliancy Group
To minimize risks and prevent data breaches, healthcare facilities need to invest in state-of-the-art cybersecurity solutions to bolster their defenses and strengthen resilience. Here are five ways that can help healthcare organizations improve their security posture in 2022.
1. Zero trust
The concept of zero trust is not new. It was coined back in 2010 by Forrester Research analyst John Kindervag. The key concept behind a zero trust architecture (ZTA) is “never trust, always verify”, meaning that all users and devices within and outside the organization must always be authenticated, authorized, and validated before they are granted access.
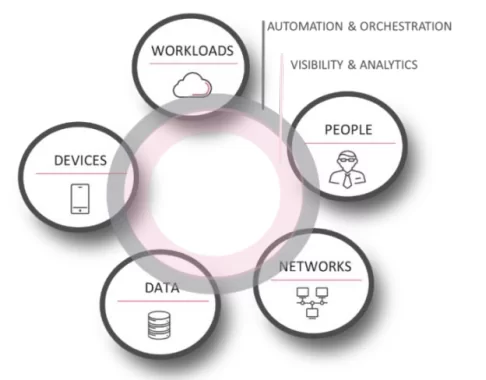
Zero trust is not a single technology but rather a cybersecurity paradigm that provides guiding principles on how to protect an organization’s data and resources. ZTA encompasses a broad portfolio of techniques and capabilities from different categories, including:
- Identity and access management (least privileged controls, multi-factor authentication, lifecycle management);
- Data security (classifying and managing data according to the risk level);
- Devices (monitoring end-points and measuring trustworthiness of devices in real-time);
- Workloads (securing applications, cloud services, containers, and other workloads);
- Network (implementing micro-segmentation, software-defined perimeter);
- Automation and orchestration (leveraging security automation, orchestration, and response (SOAR) tools);
- Visibility and analytics (monitoring and analyzing behavior of all data, users, and devices to detect anomalies);
Source: HHS Cybersecurity Program
2. Password elimination
According to the Verizon 2021 Data Breach Investigations report, compromised or stolen credentials are the primary means for hacking into an organization, accounting for 61% of all data breaches.
Cybersecurity professionals have long been pushing the need to take long-term passwords out of the picture and adopt a more secure, passwordless approach to authentication. There are a number of techniques that can make password elimination feasible like biometrics-based authentication (fingerprints or face recognition) or one-time codes sent via SMS or an authenticator app.
3. Secure access service edge
Today, healthcare ecosystems are much more complex and include cloud technology, mobile devices, connected medical devices, and remote healthcare workers. To deliver high-quality patient care, a mobile healthcare workforce needs to have timely access to critical data while still keeping it safe and protected. But implementing firewalls to protect healthcare networks and blocking external access just are no longer working in this mobile landscape.
First described by Gartner in 2019, the secure access service edge (SASE) model represents a complete shift in a cybersecurity paradigm. Instead of limiting access based on a specific location, SASE framework is designed to deliver a secure connection directly to the source (user, device, or edge computing location). The model combines software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) with security controls and delivers it as a cloud service. SASE guidelines also govern, among other things, the quality of service, dynamic routing, cost and latency optimization, and more.
4. Fully homomorphic encryption
Encryption has always been one of the core cybersecurity principles for businesses that handle sensitive personal data. And organizations go to great lengths to ensure robust data encryption in motion and at rest. The problem — and potential vulnerability — arises when the data needs to be decrypted in order to be processed.
This is where fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) comes into play. Homomorphic encryption is a type of advanced encryption that makes it possible to perform analytical functions directly on encrypted data and yield the same results as if these processes were run on decrypted files.
Imagine the situation when a researcher needs to perform a statistical analysis on a cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes but sharing personally identifiable information (PII) is against the HIPAA privacy rule. By leveraging full homomorphic encryption, a hospital can encrypt sensitive medical record data and send it to a public cloud computing platform for the researcher to run the necessary computations. And since the data is encrypted the whole time, it remains secure and protected against unauthorized access throughout the entire process.
5. Blockchain
Despite being one the biggest buzzwords of the last couple of years, blockchain is gradually revealing its revolutionary potential to disrupt entire industries, from cryptocurrency-based payment transactions to smart contracts in banking to distributed ledger technology (DLT) for e-government solutions. In fact, the global blockchain market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 26.2%, reaching $19.9 billion by 2025.
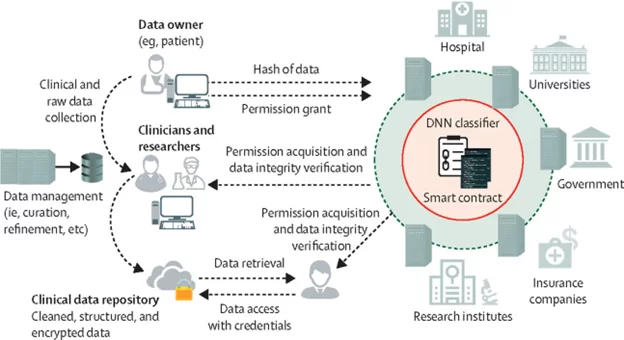
In healthcare, blockchain can become a valuable piece of the cybersecurity puzzle. Blockchain is a shared, incorruptible and digitally distributed ledger that exists across a network. Simply speaking, it is essentially a very secure database that is extremely difficult to alter or hack because data is stored not in one place but in many. By concealing any individual’s identity with complicated codes, blockchain provides a safe space for sensitive medical data. And due to the decentralized nature of the technology, healthcare providers and organizations can share information in a quick and secure manner.
Blockchain-based healthcare data management system between multiple stakeholders
Source: The Lancet
Key takeaways
The findings of numerous studies and cybersecurity reports all show one thing — the healthcare sector is inundated with cyberattacks and security-related issues. But despite the growing scale of cyber threats, many healthcare providers and institutions remain inadequately protected.
Given that an average data breach costs several millions of dollars, investing in robust cybersecurity strategies and implementing multiple layers of security must become a top priority for healthcare institutions. One of such strategies is adopting the principles of zero trust architecture to prevent malicious activity, deter ransomware, and ensure better protection of PHI. Other methods include implementing passwordless authentication, leveraging fully homomorphic encryption, and even using blockchain technology to mitigate the ever-evolving security threats.