The big data technology market is valued at $349.4 billion in 2023, with a projected market size of $1.19 trillion by 2032. Retailers use real-time analytics to optimize inventory, while healthcare uses predictive models to treat patients. Big data implementation in 2025 will be driven by a clear strategy, scalable architecture, and effective data management. Big data technology implementations allow organizations to process, store and analyze information on a large scale, making more informed decisions.
What are Big Data?
Big data implementation involves managing huge, diverse data sets—both structured and unstructured—to generate actionable insights. Banks analyze millions of transactions daily to detect fraud, and e-commerce platforms use big data to personalize recommendations. Following best practices ensures high data quality, security, and business value.
Part 1. How we struggled with big data implementation.
The whole story about big data implementation started with an ongoing project. Our team was working on a project for monitoring a range of devices: switches, routers, computers and more. The main goal of this system was to provide businesses with advanced real-time performance reporting by collecting and analyzing KPI across IT infrastructure. The project was based on classic old-school architecture, with Oracle Database used as a data storage.
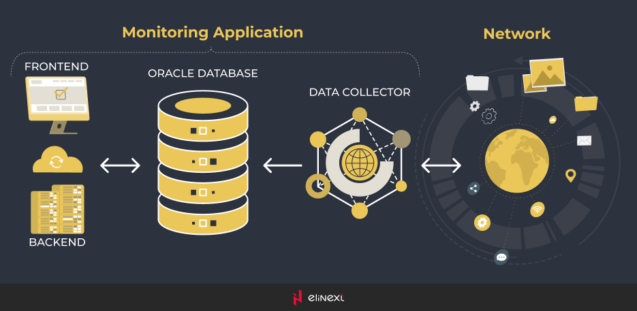
The system worked in the following way: Data Collector polled the devices via SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and stored raw data in Oracle DB. Then backend processed raw data and transformed it into the format that allowed for better data analytics. As a result, the customer was able to discover devices in the network using IP range, view statistic for selected devices for any period, build reports, charts, set up alarms and manage multi-vendor networks, systems and databases.
Challenge
Although the solution worked well for most users, some major customers had several millions of devices. The system was launched in 1998, so it had to store the detailed statistic for at least 10 years to compare results and make predictions.
Each device produced around 10 KB of data. Some new devices produced much more information, around 100-300 KB, but let’s take the average of 10 KB for calculation. Each device was polled every 1 minute, which made up 10 KB x 60 x 24 =14 MB per day, or 14 MB *365 = 5 GB per year. Assuming the customer had 10 million of devices, his devices produced around 48 PB of data per year.
Since this solution had no capabilities for horizontal scaling, it was impossible to work with such amount of data. To provide customer with the detailed statistics, we introduced some limitations on the number of devices and days. However, this solution was inconvenient for the customer.
To improve our current implementation of data storing and processing, we experimented a bit with big data technologies:
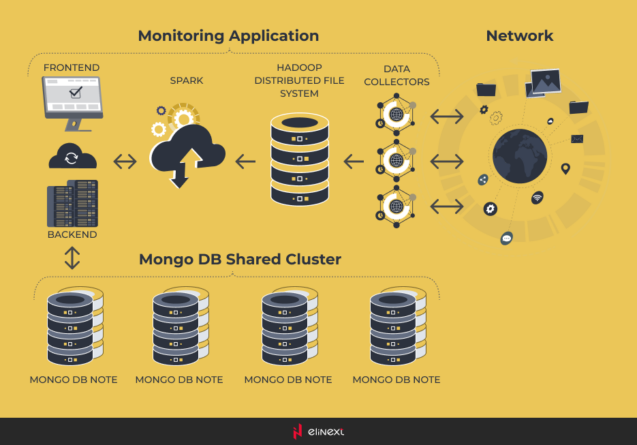
First, we decided to use MongoDB shared cluster instead of single Oracle database. This allowed client to store much more data, but the performance was almost the same, because data was collected by single data collector and processed by single backend. That’s why we also decided to implement Hadoop Distributed File System (HFDS) for raw data storage and Hadoop’s MapReduce for data processing to store it in MongoDB.
After tool research on the market, Hadoop MapReduce was replaced with Apache Spark, as it was easier to use and allowed running programs faster.
As a result, we received a system with multiple data collectors installed on several segments of the network, HDFS, Spark, and MongoDB. We emulated the monitoring of 4 million of devices and haven’t detected any problem neither in the performance of the system nor in data storage capabilities. As a comparison, the initial implementation without Big Data was able to monitor up to 100,000 devices only, so we can talk about significant system improvement.
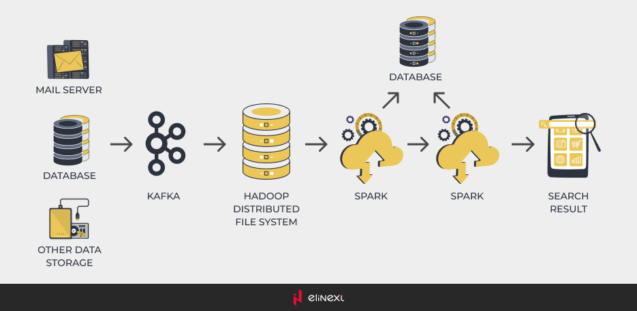
According to our implementation plan, the next step was to bring Kafka in our project and add a search engine (we were thinking about either Elasticsearch or Solr). What is more, since the project scaled significantly, we were considering to replace MongoDB with Cassandra for its column-oriented database.
However, our big data experiment was stopped, as the client decided to put the project on the shelf and engage Elinext dedicated team that worked on this project in building the product of a similar kind, but with more functionality.
“Big data implementation best practices start with clear objectives, scalable cloud infrastructure, and continuous data quality monitoring. For example, our clients get analytics three times faster and save 40% by automating data pipelines and ensuring control at every stage.”
— Elinext Big Data expert
Part 2. Top questions you should ask before starting big data application.
A lot of questions may arise when coming up with a big data strategy. The answers depend on the amount and type of data and the goals you want to achieve with its exploration. We asked our IT Services Director Alexey Trigolos to share the general questions appearing on the way of big data implementation.
1. Do you really need big data?
Having once used big data related technologies, you may be tempted to use them everywhere, in each project. Don’t do this. Choose only most suitable stack of technologies required for your solution. I have seen several CRUD-like application, where the customer or developer switched to using HDFS, Spark, etc. hoping to get more productive and flexible solution. As you can guess, he didn’t get anything but a headache.
2. How to choose right technologies or frameworks?
The world of big data offers a lot of frameworks: HDFS, Spark, Flink, Mahout, Tez, Storm, Sanza, etc. You need to investigate what problems you need to solve and choose most suitable and modern frameworks that are efficient, economical and meet your business requirements.
3. What resources are needed for your environment?
Unlike ‘classic’ applications, big data application requires much more resources, for horizontally scalable database, distributed file system, distributed computing, data-mining, etc. In most cases, cloud-based solution will be preferable, otherwise take care of maintenance and support of your environment.
4. What is your data?
In big data application, the data is almost always unstructured or semi-structured. Furthermore, most of your data is useless and the only relatively small proportion contains useful information. It’s required to analyze what information you need to operate, what internal structure it may have and how to organize the data for the further processing and computing.
5. How to take care of data security?
Due to distributed architecture of your application, the data will be walking between nodes of your application. Many consider storing big data dangerous, as it can contain sensitive information like emails, payment card numbers, or other personal information. The communication channels inside your distributed application should be secured to fit safety policies of your customers.
Discover the power of data!
Order big data implementation best practices for your company to increase ROI, reduce costs and gain a competitive advantage in the data-driven world of 2025.
Part 3. Big Data frameworks and technologies stack that we suggest.
Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is a framework for running applications on large cluster built of commodity hardware. Indeed, Hadoop is the standard for big data processing. The product we decided to exploit in our project of is Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) that stores data on the compute nodes, providing very high aggregate bandwidth across the cluster.
Kafka
Apache Kafka is a distributed system used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming apps used for processing logs, metrics, and collections. We have chosen this technology for its horizontal scalability, fault-tolerance, and high speed. Within our project, Kafka was used for data retrieval from the mail servers. The data received was consequently put into Hadoop distributed file system for storage.
Spark
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing which is all-compatible with Hadoop. We preferred Spark to MapReduce for our project’s purposes because of higher speed of big data processing and ease of deployment. Moreover, Spark allows for iterative machine learning algorithms with each iteration contributing to the overall results.
MongoDB and Cassandra
Our choice of MongoDB was determined by its well-supported integration with Hadoop and its aggregation framework. It helped us store data in convenient form for processing.
Cassandra caught our interest as a possible replacement of MongoDB within our project because of its support for dynamic columns and distributed counters. We also were impressed by its scalability and reasonable costs of ownership.
Elasticsearch and Solr
Both search platforms are built on top of Apache Java library Lucene, so many of their functionalities and their search capabilities are relatively similar. However, Elasticsearch is considered to be easier to use and better for analytical queries and distributed indexing, while Solar is well-oriented in everything connected with text search and is popular for being consistently documented.
How Big Data Engineers from Elinext Can Help Your Business
Big data implementation and big data technology implementations by Elinext deliver end-to-end solutions: data integration, real-time analytics, and AI-powered analytics. Elinext helped a telecommunications company reduce customer churn by 25% using predictive analytics. The company’s engineers develop scalable architecture, automate ETL processes, and ensure compliance, allowing customers to achieve cost savings of up to 45% and rapid ROI. Elinext’s expertise turns raw data into a driver for business growth.
Conclusion
Best practices for big data implementation – clear goals, scalable platforms, and effective governance – are critical to success. Manufacturers are using IoT data to optimize production, and healthcare is using it for personalized medicine. Elinext’s big data technology implementations ensure data quality, security, and actionable insights, helping companies thrive in a data-driven competitive environment.
FAQ
What is big data implementation?
Big data implementation involves deploying systems to collect, store, and analyze large amounts of data to generate insights. Banks use big data implementation best practices to detect fraud in real time, improving security and customer trust.
Why is it important to follow best practices?
Following big data implementation best practices ensures data quality, security, and return on investment. A retailer that uses standardized data pipelines and management systems avoids costly mistakes and gets faster, more reliable business insights.
What is the first step in implementing big data solutions?
The first step is to define clear business goals and data requirements. A hospital starts by defining key metrics like patient wait times before selecting big data tools and creating analytics pipelines.
What’s the best way to store big data?
Big data implementation favors scalable cloud storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Data Lake) for flexibility and cost efficiency. E-commerce companies store clickstream data in the cloud, which allows for real-time analytics and rapid scaling of data.
How do you ensure data quality in big data projects?
Ensuring data quality in big data implementations includes automated validation, cleansing, and governance. Telecom companies use ETL tools to filter out duplicates and errors, ensuring accurate analytics and reliable business decisions.







